Description
Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that is widely used for the treatment of pain, fever, and inflammation. It is available in various forms, including tablets, capsules, suspensions, and topical gels. Ibuprofen works by inhibiting the enzyme cyclooxygenase (COX), which is responsible for the production of prostaglandins – chemicals that cause inflammation, pain, and fever.
Mechanism of Action
Ibuprofen’s mechanism of action is based on its ability to inhibit the enzyme cyclooxygenase (COX). There are two main isoforms of COX: COX-1 and COX-2. COX-1 is responsible for the production of prostaglandins that maintain normal physiological functions, while COX-2 is responsible for the production of prostaglandins during inflammation, pain, and fever. Ibuprofen inhibits both COX-1 and COX-2, leading to the reduction of inflammation, pain, and fever. However, it is essential to note that selective COX-2 inhibitors, such as celecoxib, have been developed to minimize the risk of gastrointestinal side effects associated with COX-1 inhibition.
Uses and Dosage
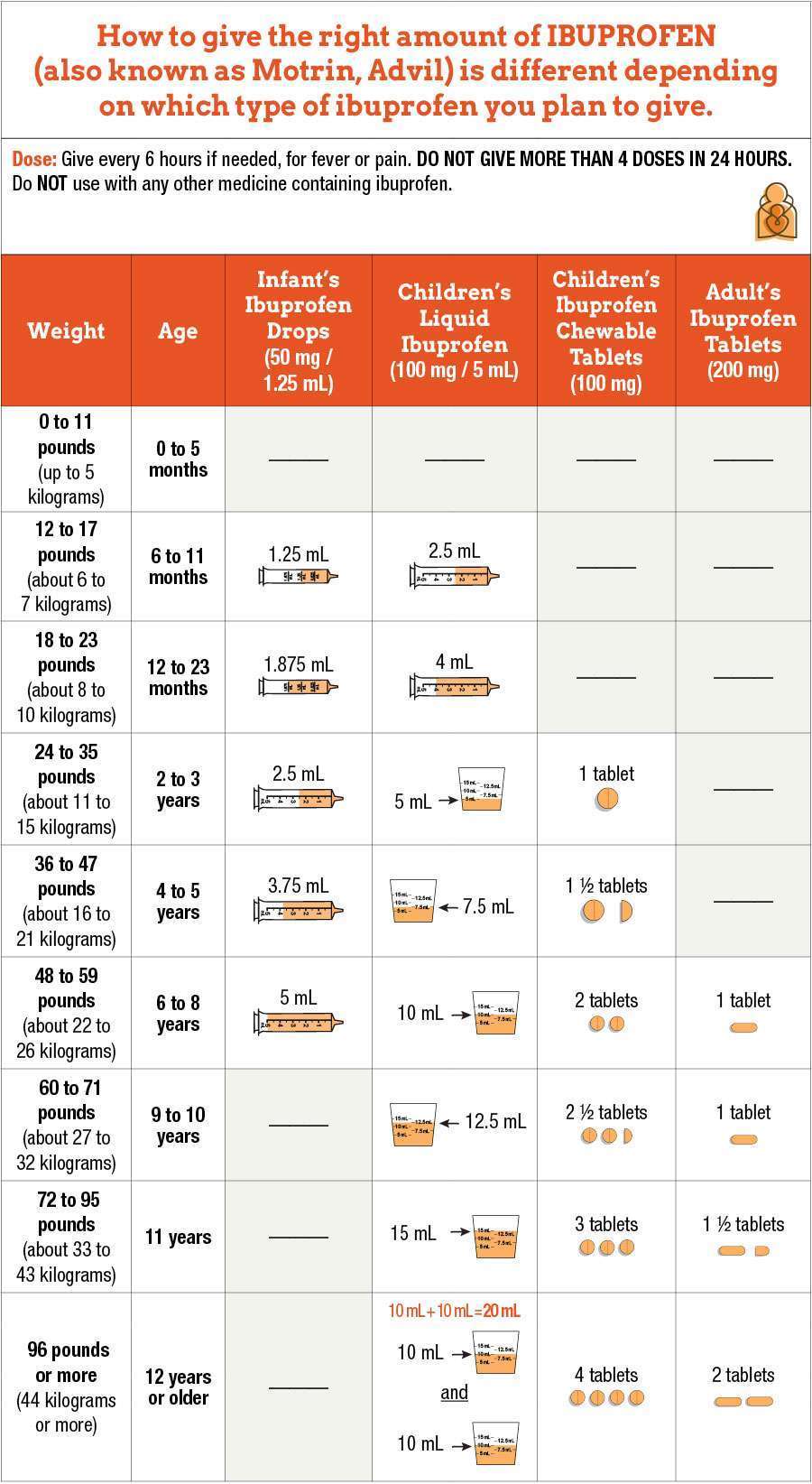
Ibuprofen is used to treat various conditions, including headaches, muscle aches, toothaches, menstrual cramps, and minor injuries. It is also prescribed for the management of mild to moderate pain and fever. The dosage of ibuprofen varies depending on the age of the patient, the condition being treated, and the form of the medication. Typically, adults can take 200-400 mg every 4-6 hours, not exceeding 3200 mg per day. Children’s dosages are lower and should be determined by a healthcare professional.
Side Effects and Precautions
Like all medications, ibuprofen can cause side effects. Common side effects include gastrointestinal problems, such as stomach pain, heartburn, and nausea. More severe side effects, although rare, can include kidney damage, liver damage, and an increased risk of heart attack or stroke. Ibuprofen should be used with caution in individuals with a history of gastrointestinal problems, kidney or liver disease, heart disease, or asthma. Pregnant women and breastfeeding mothers should consult their healthcare provider before using ibuprofen.
Conclusion
Ibuprofen is a widely used NSAID that effectively treats pain, fever, and inflammation. Its mechanism of action involves inhibiting both COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes, leading to reduced inflammation and pain. It is essential to follow the recommended dosage and consult a healthcare professional for potential side effects and precautions.
Authoritative Reference Titles
British National Formulary (BNF): A comprehensive, up-to-date, and authoritative source on medications, including ibuprofen, used in the United Kingdom. It provides information on the uses, dosage, side effects, and precautions of medications, making it an essential reference for healthcare professionals and patients.
American College of Rheumatology (ACR): A professional organization dedicated to advancing rheumatology knowledge and practice. The ACR guidelines on the use of NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen, in the management of rheumatic diseases are widely recognized and respected.
The Merck Manual: A leading medical resource used by healthcare professionals and patients worldwide. The Merck Manual provides comprehensive information on various medical topics, including the use of ibuprofen for pain relief and its potential side effects and precautions.
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.